IP Protection Rating of Luminaires
Difference Between Indoor and Outdoor Lamps and Lanterns
The main difference is that the installation location is different. For example, indoor lamps can be installed on the ceiling and wall, but outdoor installations often lack ceilings and walls, and may be installed on the ground. Of course, some outdoor lamps and lanterns are also mounted on walls, but the biggest difference is that indoor spaces have roofs to protect from wind and rain, whereas outdoor spaces do not.

Therefore, for outdoor use, outdoor luminaires must have strict dust and waterproof requirements. The degree of protection of the enclosure is classified according to the level of dust and moisture, usually using the protection class code IP.
IP Protection Class Code
The code indicating the level of protection usually consists of the characteristic letter IP and two characteristic numbers. The first digit refers to dustproof; the second digit refers to waterproof.
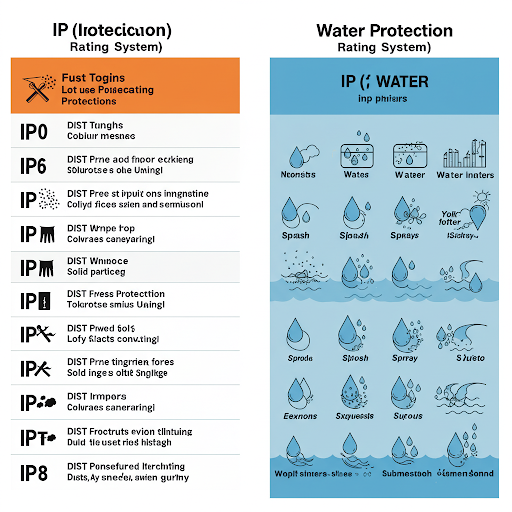
First Digit: Dust Protection
| First Digit | Brief Description | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No Protection | No special protection |
| 1 | Protection Against Solid Foreign Objects >50mm | Prevents entry of solid foreign objects with a diameter greater than 50mm. Prevents accidental or incidental contact with live parts inside the enclosure by a large area of the human body, but does not prevent deliberate proximity. |
| 2 | Protection Against Solid Foreign Objects >12mm | Prevents entry of solid foreign objects with a diameter greater than 12mm and a length not exceeding 80mm. Prevents contact with live parts or moving parts inside the enclosure by fingers. |
| 3 | Protection Against Solid Foreign Objects >2.5mm | Prevents entry of solid foreign objects with a diameter greater than 2.5mm. Prevents contact with live parts or moving parts inside the enclosure by tools, metal wires, etc. with a thickness (diameter) greater than 2.5mm. |
| 4 | Protection Against Solid Foreign Objects >1mm | Prevents entry of solid foreign objects with a diameter greater than 1mm. Prevents contact with live parts or moving parts inside the enclosure by tools, metal wires, etc. with a thickness (diameter) greater than 1mm. |
| 5 | Dust Protection | Cannot completely prevent dust entry, but the amount of entry cannot hinder the normal operation of the equipment. |
| 6 | Dust-Tight | No dust entry. |
Second Digit: Water Protection
| Second Digit | Brief Description | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No protection | No special protection |
| 1 | Protection against vertical dripping water | Dripping water (vertical dripping) has no harmful effect |
| 2 | Protection against vertical dripping water (15°) | When the enclosure is tilted at an angle of 15° from the normal position, vertical dripping water has no harmful effect |
| 3 | Protection against vertical spraying water (60°) | Exposure to water spraying at an angle of up to 60° from the vertical has no harmful effect |
| 4 | Protection against splashing water | Exposure to water splashing in any direction has no harmful effect |
| 5 | Protection against spraying water | Exposure to water spraying in any direction has no harmful effect |
| 6 | Protection against sea water spray | When exposed to strong waves or strong jets of water, the amount of water entering the enclosure does not reach a harmful level |
| 7 | Protection against temporary immersion | When immersed under specified pressure and for a specified duration, the amount of water entering the enclosure does not reach a harmful level. Capable of long-term underwater operation according to the conditions specified by the manufacturer |
| 8 | Protection against continuous immersion | Note: Usually refers to a waterproof type, but for certain types of equipment, water ingress may be allowed up to a non-damaging extent |
Classification of Outdoor Lighting Fixtures
Generally speaking, for outdoor lighting, we will be divided into three categories: architectural lighting, landscape lighting, and functional lighting.
The traditional outdoor lighting is to make a cavity and put the light source in it to protect it and support it so that it can work properly. The LED era is no longer to do the cavity, but through the use of lenses and other light out of the guide, which is similar to the concept of indoor lighting, but outdoor lighting is more focused on waterproof and dustproof protection.
Commonly Used Architectural Lighting Fixtures
- Floodlight
- Wide beam: Uniform illumination over a large area.
- Floodlights will throw light out over a large area, illuminating a large area of the building facade.
- Narrow beam lighting: Floodlights and spotlights serve the same purpose, illuminating the building from a distance. However, floodlights are wide-beam and spotlights are narrow-beam, just as indoors, downlights are wide-beam and spotlights are narrow-beam. Floodlights and spotlights are, by definition, different beam angles. Generally speaking, they can be common a lamp housing, as long as the replacement of the optics can achieve a narrow in the wide and other different angles of light effect. And depending on the illuminated object, different mounting brackets can also be selected.

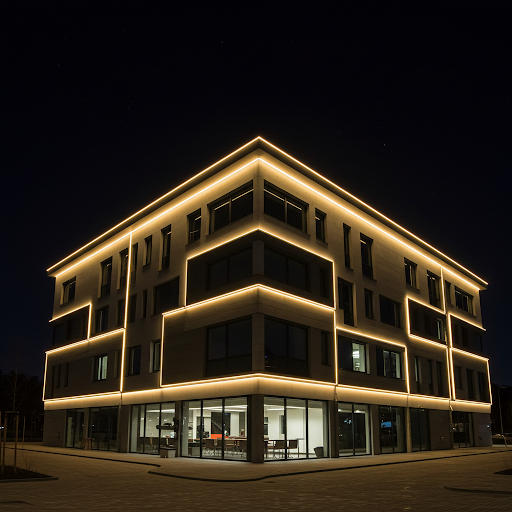
- Linear Floodlights
- Suitable for all kinds of wall washing lighting.
- LED light source, choose the power according to the demand, ranging from 8~100W.
- In the LED era, in addition to square, round, etc., there are also linear floodlights, which are long, such as 1 metre long, 1 metre 2 long, the width of which may be 50, 80, you can linearly illuminate the building, but of course there are also short, you can go to do splicing.
- Like the role of the picture below is to throw the light out to illuminate the building, such as railings, walls and these details.
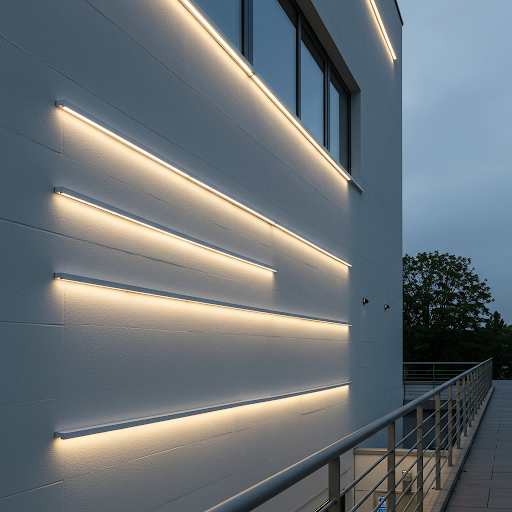

- Outline Lighting
- Contour lighting: outlining.
- Contour lighting also grows into a linear shape, but instead of casting light out, its role is to shine on its own. It can be used for contour lighting of buildings, which is what we often refer to as outlining.

- Buried light
- Suitable for sculpture, building façade, scenic wall and other decoration and lighting.
- The light source is selected according to the illuminated object, the size varies.
- Buried lights are hollowed out a hole in the ground, the lights embedded in it, its surface and the ground is almost flat, this buried lights are often used to do sculpture or wall lighting.
- For example, large buried lights, can illuminate a large area of the wall. Medium-sized buried lights can be used to illuminate a tree.
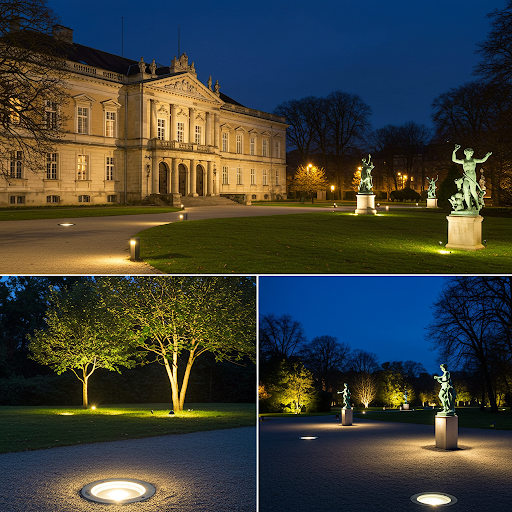

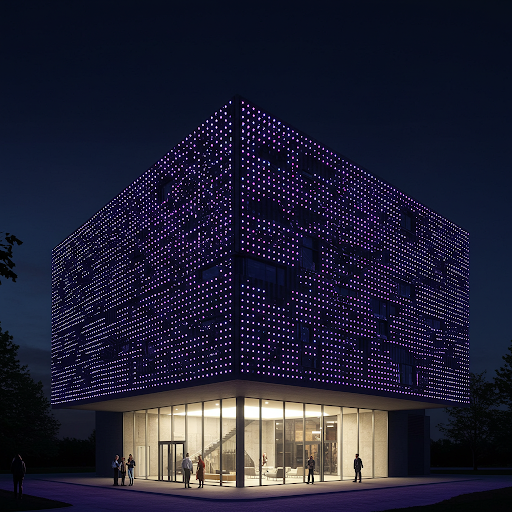
- Point light source
- Surface mounted, usually used in architectural night lighting, can achieve monochrome, colour changing, and video playback and other functions of the lighting effect.
- Some lamps and lanterns are surface mounted, directly to the people see a point, we call it a point light source, it is generally not large in size, mounted on the building, see is not very clear, but it is lit up at night, its point of light is revealed.

- Wall lamp
- Wall surface installation, widely used in architectural lighting or the need to create a special lighting effect of the façade, etc., there are a variety of lighting effects such as unilateral luminous, upper and lower sides of the luminous and space around the luminous.
- Outdoor is nothing more than the ground and the wall, so wall lamps are often installed in the building, emphasising the different shapes of the whole building effect, for example, some wall lamps can be painted on the wall of a flower.
- Floor Lamps
- Sub-embedded installation and surface mounting, used in building facades, underground car park entrances and exits, parks and other places, embedded need to be pre-embedded, and attention should be paid to the installation height.
- Also mounted on the wall, there is a light called footer light, its role is not to illuminate the surface of the building, but mounted on the wall, down to illuminate the ground.

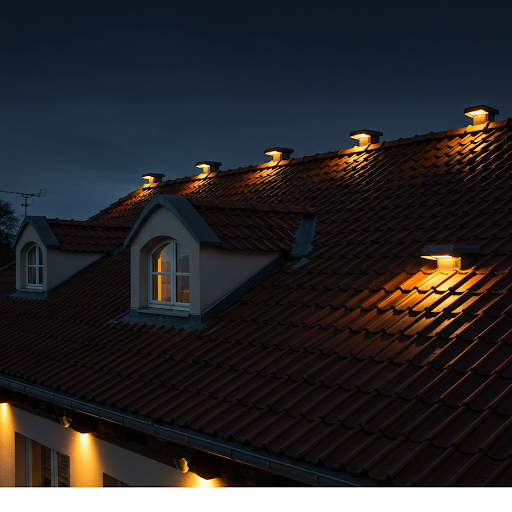
- Tile Light
- Using LED light source, bracket mounted.
- Widely used in ancient architectural roof tile lighting, low-voltage power supply.
- The whole lamp power of about 5W.
- There is also a frequent illumination of the roof of the building called tile light or corrugated light, it can be installed in the front of the tile, the whole tile lighting.

Commonly Used Landscape Lighting Fixtures
- Yard light
- Suitable for parks, neighbourhoods and other wider pavement road lighting.
- Light source: 10~20W LED or more than 20W traditional energy-saving lamps, metal halide lamps.
- Light pole: 3~5m-4m.
- Garden light a lamp can illuminate a yard, it is generally high, in the courtyard about 3, 5 metres high. A pole above a lamp head, there are a variety of forms, it shines a little larger.
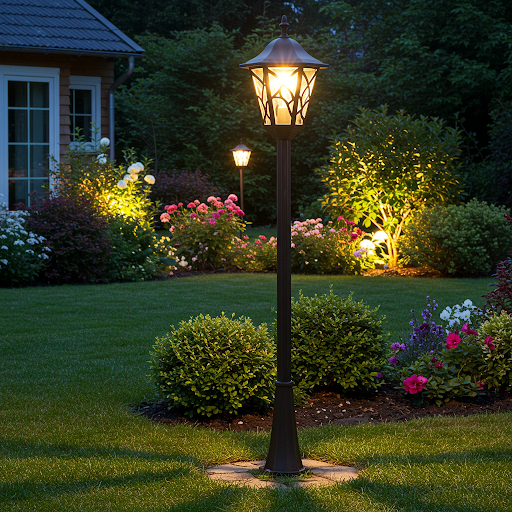
- Lawn lamp
- Small lawn lamps: suitable for small traffic, quiet road lighting.
- Light source: 6W LED or 10W energy-saving lamps.
- Lamp height: 0.3-0.8 metres.
- The shorter one is called lawn lamp, this kind of light range is small, mainly to light up the road near the grass.
- Medium-sized lawn lamp: suitable for parks, neighbourhoods and other narrow pavement lighting.
- Light source: 6-10W LED or 10-20W energy-saving lamp.
- Lamp height: 0.6-1.2 metres.
- There are also slightly larger, such as one metre high lawn lamps used in some public areas, illuminating a slightly wider pavement, the brightness will be slightly brighter than the shortest lawn lamp.
- Small lawn lamps: suitable for small traffic, quiet road lighting.

- LED buried lights
- LED era of buried lights, due to the characteristics of the light source, you can do a lot of shapes, such as the traditional common round, you can do square, rectangular, but also according to the conditions to do the integration of lamps and lanterns, such as the square on the square of the same size as the square tiles of the lamps and lanterns. Lamps need to be installed with pre-buried parts, using low-voltage power supply.
- Courtyard will also be used in the buried lights, in addition to the round kind, and the following picture of this square, long, it can be made with the tiles almost, looks inconspicuous during the day, the night will glow.

- Side-illuminated buried lights
- Special effects buried lights, the direction of light for one or both sides.
- Create a special light spot effect, in the road or square installation.
- LED light source, lower temperature, can be used for activities square, wooden platform and other places.
- Side-illuminated buried lights are also buried in the ground, can be sent to both sides of the light, for example, like the middle of the channel buried in a row of lights, its light is illuminated on both sides of the wall.

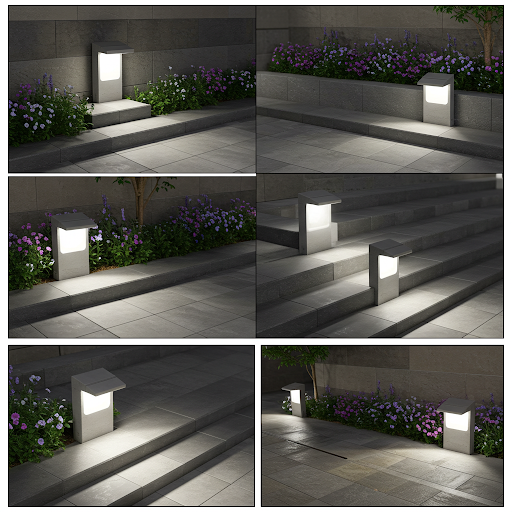
- Embedded step light
- Suitable for pedestrian lighting in the corners of walls, flower beds side, steps and so on.
- If installed on the steps, it is recommended that the installation position: the edge line of the step is aligned with the centre of the lamp.
- Like just mentioned in the architectural lighting in the footlights, the courtyard is also often used, it is in addition to square, rectangular, etc., there are a variety of shapes, but its purpose is the same, in order to illuminate the ground, to provide a normal walking lighting.

- Polarised buried lights
- Special effect buried lights, the direction of the light out of the one-way wall washing.
- Pavement mounted to illuminate the wall.
- Using LED light source.
- Buried lights in addition to direct upwards, or show a point of light, there is also the following picture of this polarised, it can light up a wall, you can light up a piece of vegetation.

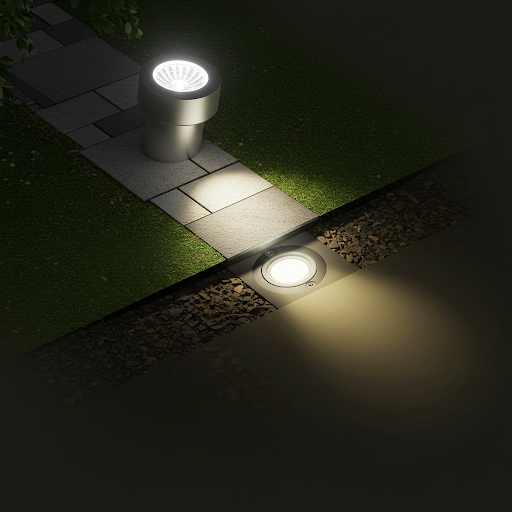
- Small buried point of light
- Small buried light point, using LED light source.
- Suitable for plaza, road accent lighting, power is generally less than 1W.
- Buried lights and a very small point of light type, generally used to do embellishments, such as the underground this point of light is a point source of buried lights caused.

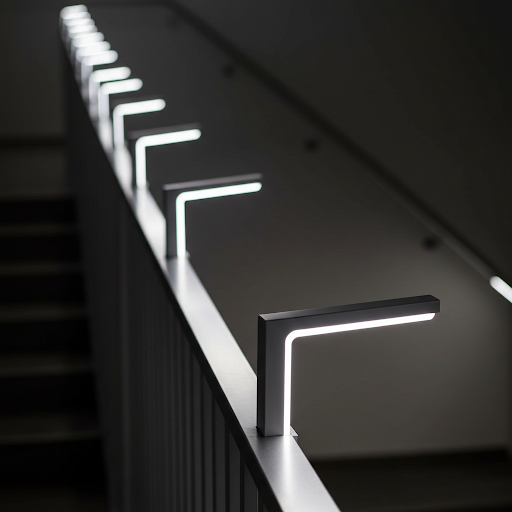
- Line guardrail light
- Mounted on the guardrail.
- Specifically mounted on the guardrail lights called guardrail lights, a line type, or mounted on the stair railings.

- Underwater lights
- Widely used in water features, fountains, swimming pools and so on.
- There are two ways, such as embedded installation and surface installation.
- Embedded lights have installation pre-installation, using low-voltage power supply.
- In the garden landscape, in order to illuminate the water will put the light into the water. Earlier we talked about IP when talking about long-term diving, your IP protection level IP68, some underwater lights are placed directly there, some have to pre-do a hole to embed it.

- Recessed pool light
- Applicable to large swimming pools, tall fountains and other decoration and lighting.
- When arranged continuously, the spacing of the lamps and lanterns should be more than 2 metres.
- Generally use LED light source, power greater than 10W.
- For example, on the pool side, generally speaking, it will be pre-opened holes, and then embedded lights, because the pool is unlikely to be installed.

- Pool Lights for Open Installation
- Suitable for deep water (>300mm) pool bottom, fountains, waterfalls, streams and other underwater lighting.
- LED light source, recommended power > 10W.
- But in the ornamental pool mounted is no problem, because mounted in the water, you do not feel ugly, because usually invisible, only it lights up you can see. But if it is a pool, people will go in, which will hurt.
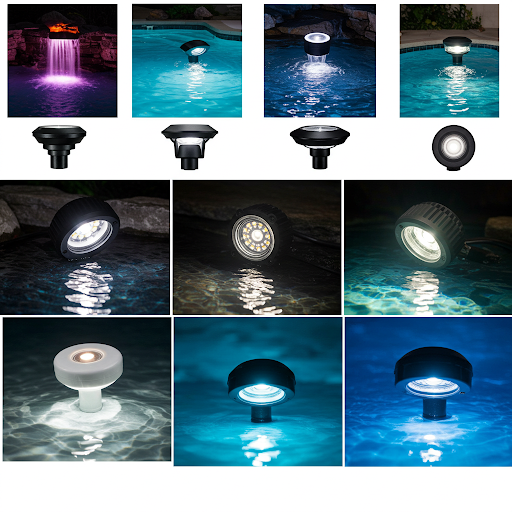

- Ring gushing lights
- Adopting LED light source, the general power is 6~12W.
- Suitable for gushing spring (gushing height <600mm) lighting.
- For fountains, fountains will have a light, ring-shaped fountain light this light is a circle on the side, the middle is empty, so that the mouth of the fountain in the middle of the spray out, so you can turn the circle to light up the fountain.

- Light strip
- Widely used in outdoor concealed places.
- For example, the square steps, waterfront platform.
- LED light source, power between 3 ~ 12W/m.
- Strip light is also often used in landscaping, where attention should be paid to the people can touch the place, do not use high-pressure, to use low-pressure, better protection.

- Large footlights
- For inconvenient installation of other lamps and lanterns at the road lighting (such as garage entrances and exits), the centre of the lamp from the ground at a height of 300 ~ 500mm.
- There are some places for road lighting, or for car lighting, we need to use larger footlights.
Commonly Used Functional Lighting Fixtures
What is functional lighting? It is the outdoor lamps and lanterns that must meet the standard requirements.
- Street Light:
- Suitable for lighting driveways with heavy traffic.
- Light source: above 150W metal halide lamp, high pressure sodium lamp or above 100W LED light source.
- Light pole: height 6m-12m.
- The national standard has a provision that the road to achieve what kind of brightness standards, usually we commute to work on the road to see the street lamp is this type of street lamp, street lamp lamp pole is generally higher, at least 6 metres, 8 metres or more, the big road may be 12 metres, 14 metres are there.
- Tunnel Light
- Applicable to urban tunnels\ tunnels through the mountains and tunnels across the river.
- Light source: fluorescent lamp, high pressure sodium lamp or LED light source.
- Installation: top or side mounted.
- Illumination: Downlight or backlight.
- If the road goes through a tunnel, you can’t put up a high pole, so we can install the tunnel light on the top of the tunnel.
- Stadium Lights
- Suitable for football field, tennis court and other places that need high pole lighting.
- Light source: 250W or above metal halide lamp, or 200W or above LED.
- Light pole: Height generally > 8 metres.
- Playing places also have regulations on what kind of illumination must be achieved in order to play here, so it is also often used floodlights, floodlights. Of course, some of the light distribution is more special, for example, the light distribution of the tennis court is more special, to meet the lighting of the entire site.
Notes on Selecting Outdoor Lighting Fixtures
Landscape lighting: pay attention to modelling, glare
Architectural lighting: pay attention to glare, maintenance, hidden.